Quick Menu
- RISING SUN 3D - ON DEMAND 3D PRINTING
- Ak Interactive
- All Game Terrain
- Ammo by MIG
- Army Painter
- Backpacks and Carrycases
- Bifrost Airbrush Paints
- Coming Soon!
- Connectors
- Chargers
- Gift Cards
- Laser Cutter, Engravers and CNC
- New Items
- Painting Brushes and Tools
- Sale!
- Services
-
- SMS - Premium Acrylic Lacquer Series
- SMS - Pearl Acrylic Lacquer Series
- SMS - Auto Colour
- SMS - Brush Series
- SMS - Cements & Adhesives
- SMS - Colour Sets
- SMS - Colour Shift Acrylic Lacquer Series
- SMS - Crystal Acrylic Lacquer Series
- SMS - DragonAir Airbrushes
- SMS - Effects Acrylic Lacquer Series
- SMS - HyperChrome Series
- SMS - Infinite Colour - Water Based
- SMS - Masking Series
- SMS - Metallic Acrylic Lacquer Series
- SMS - Precision Tools Series
- SMS - Primer Series
- SMS - Thinners, Additives and Paint Remover
- SMS - Weathering Series
- SMS - Wildlife Colours
- STEM
- Trading Card Games
- The Used
- X Class Gear
- Blogs
RC Link
79 products
Showing 1 - 48 of 79 products
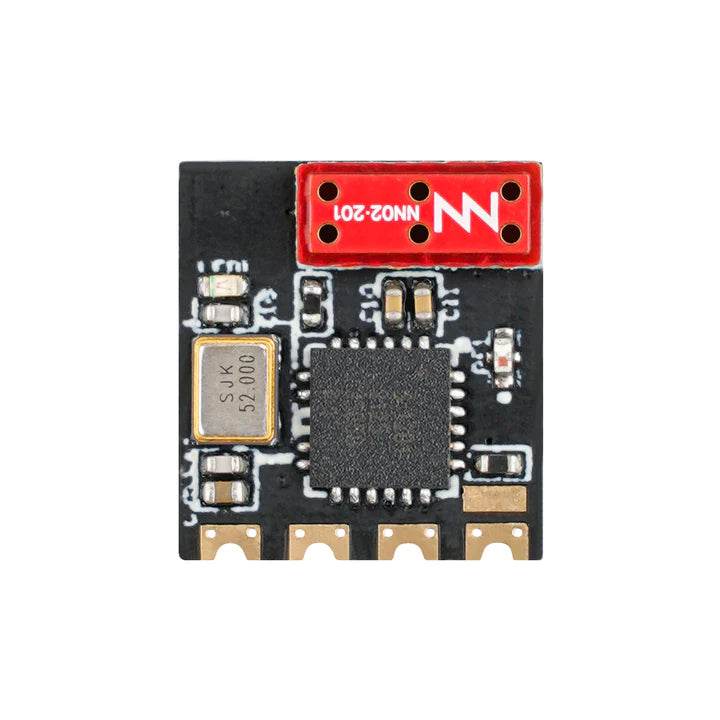
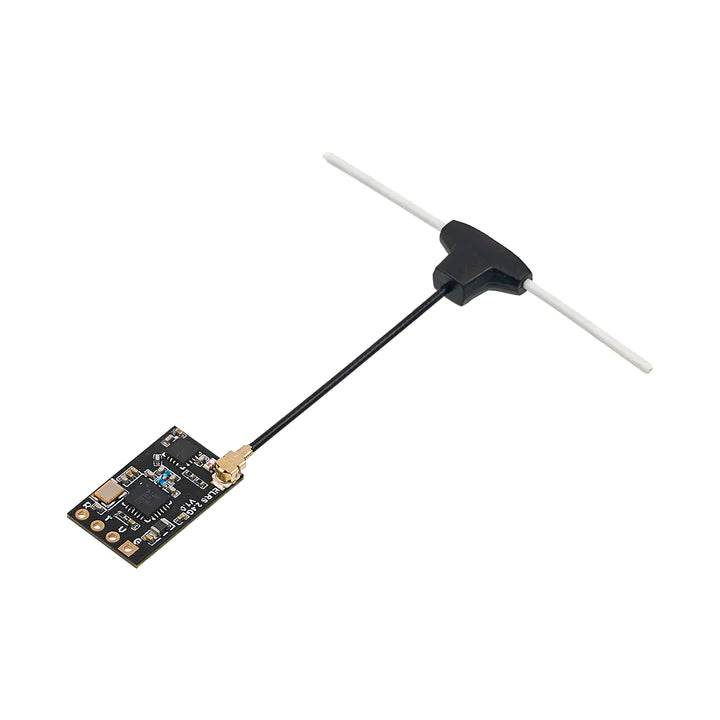
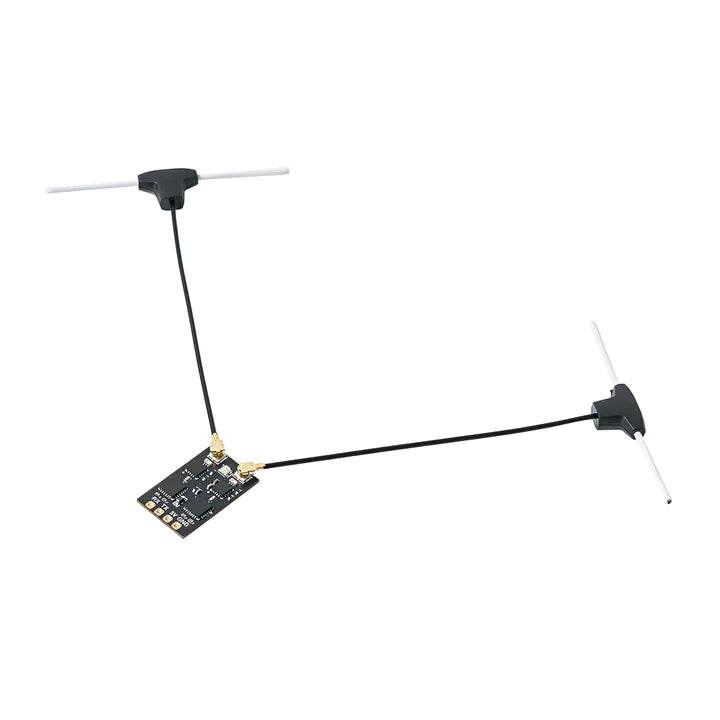
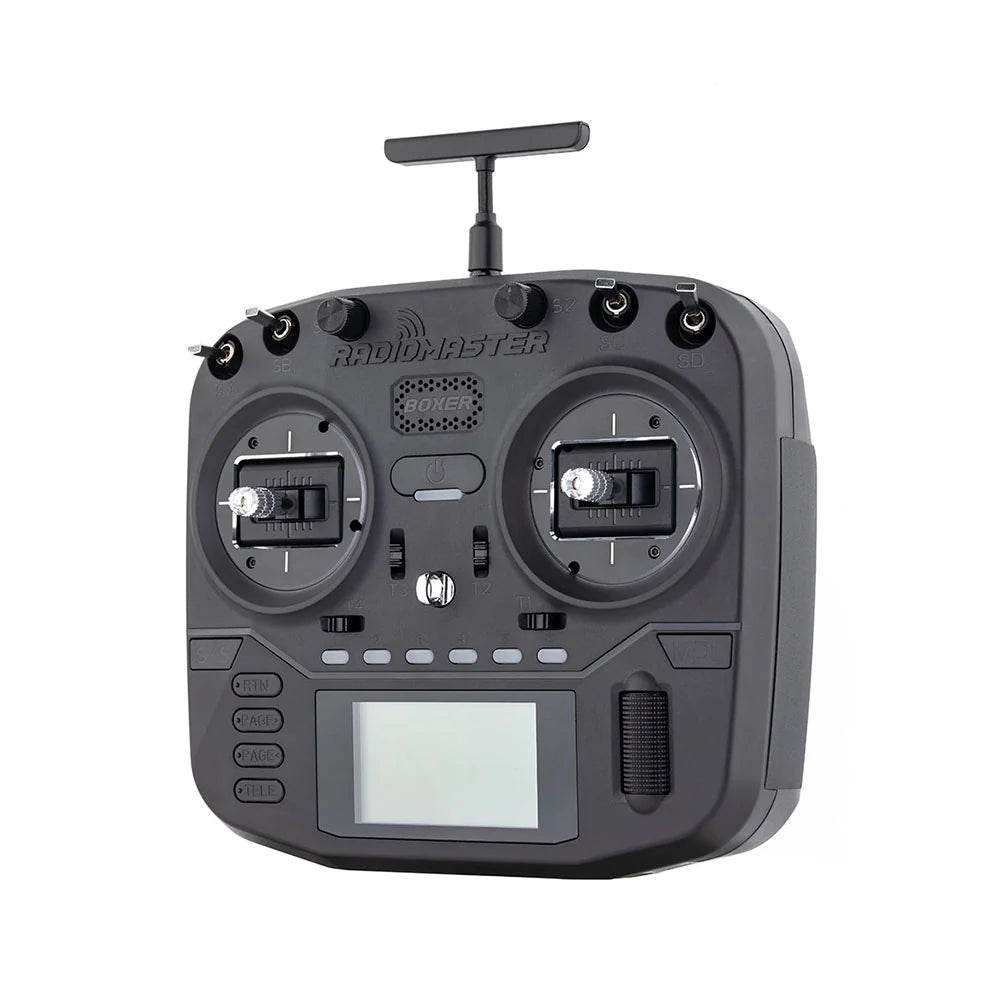
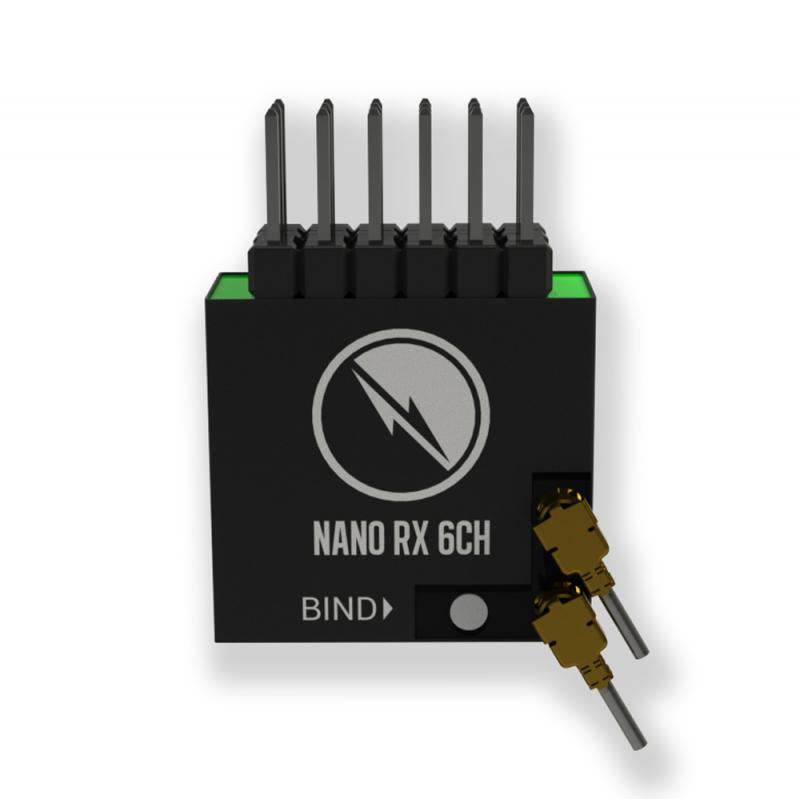
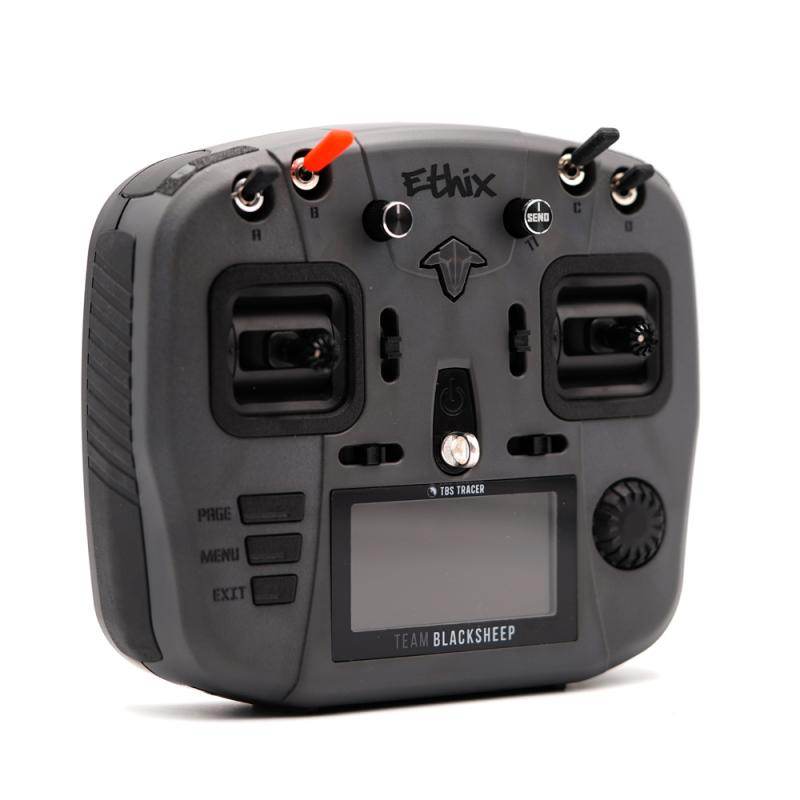
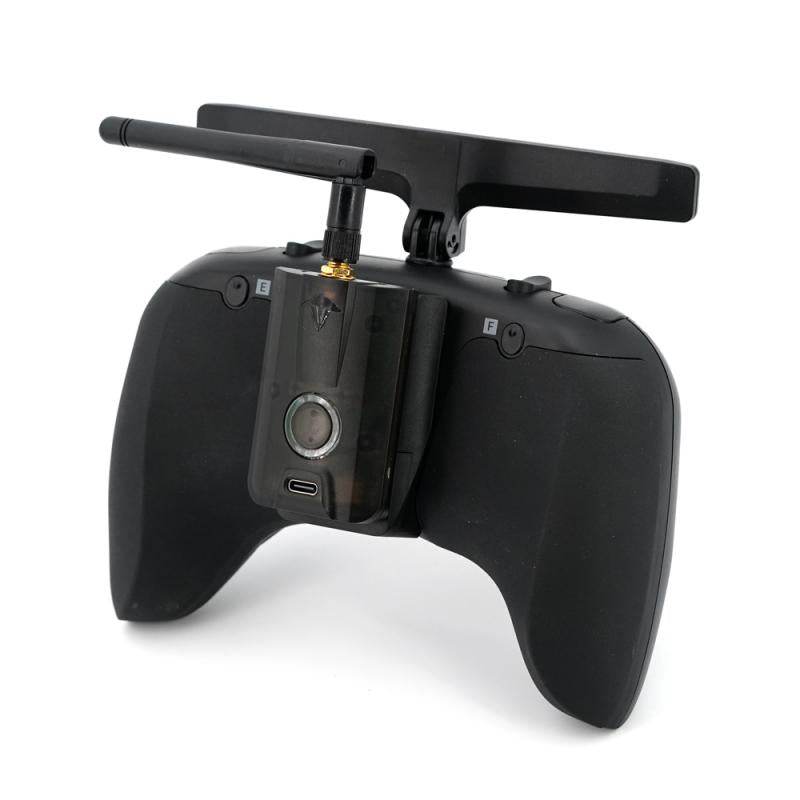
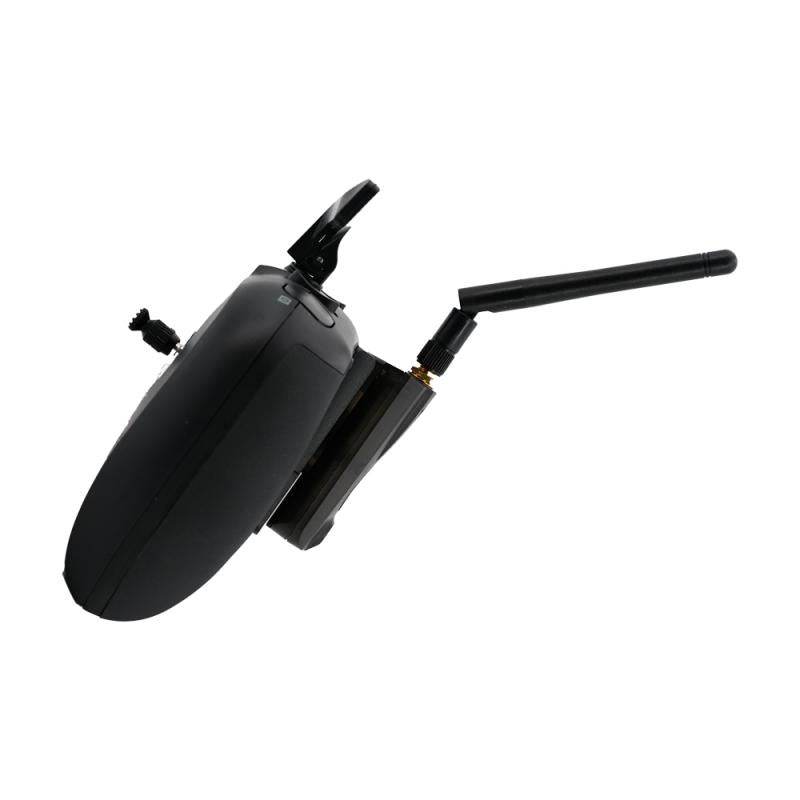
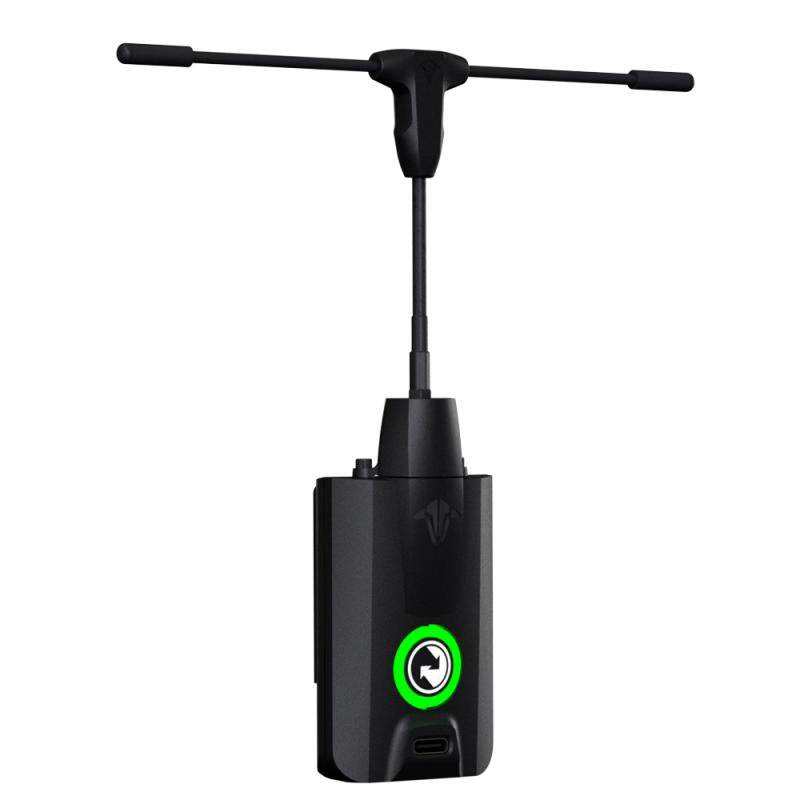
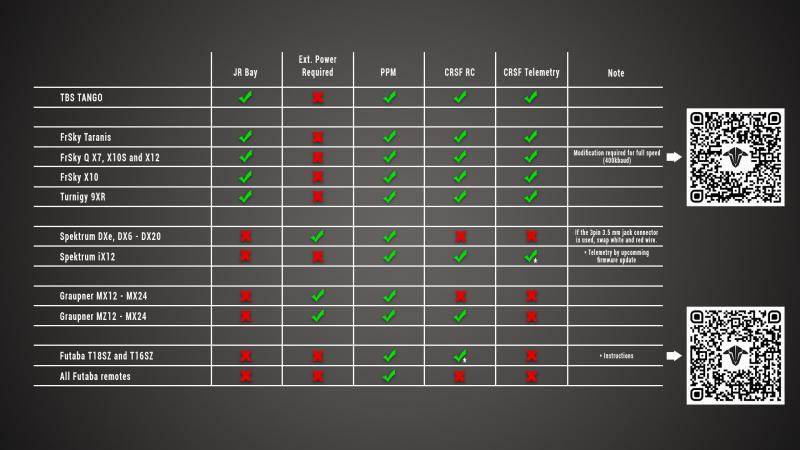
RC Link – Reliable Radio Connections for FPV Drones
Strengthen your control with professional-grade RC Link systems from Rising Sun FPV.
We offer transmitters, receivers, antennas, and link systems optimized for reliability, low latency, and long-range performance.
Compatible with ExpressLRS, Crossfire, Tracer, and more.
Stay connected — shop RC Link solutions today at Rising Sun FPV.
Showing 1 - 48 of 79 products
Display
View
Save $3.00
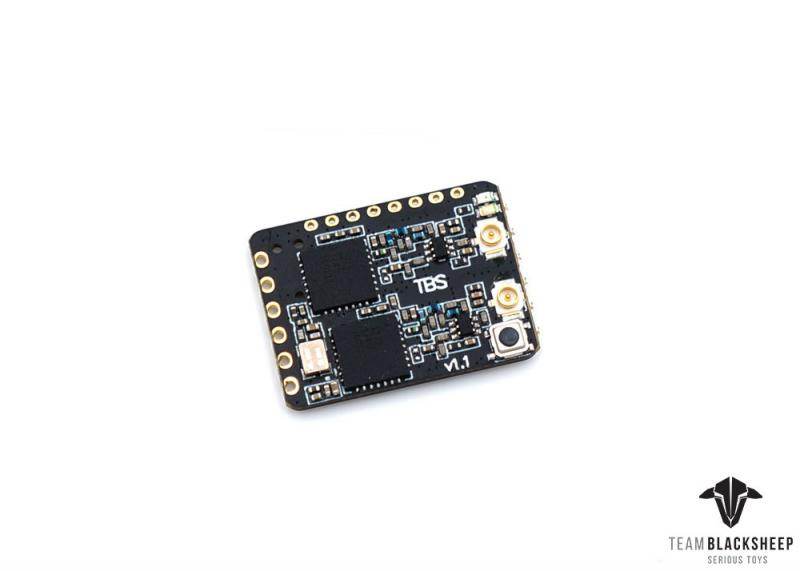

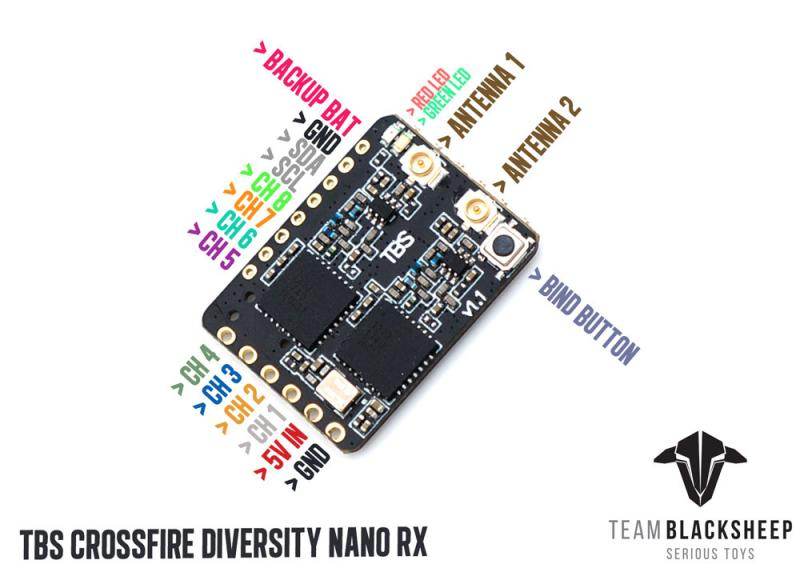
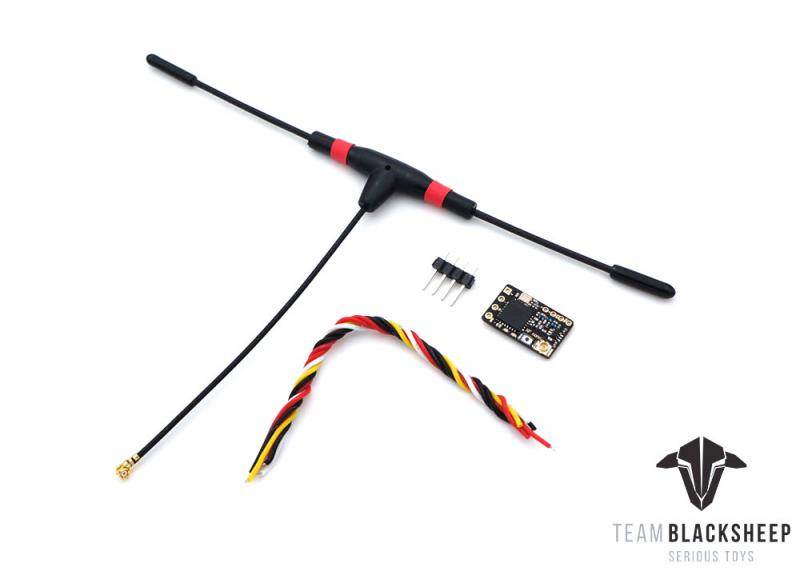
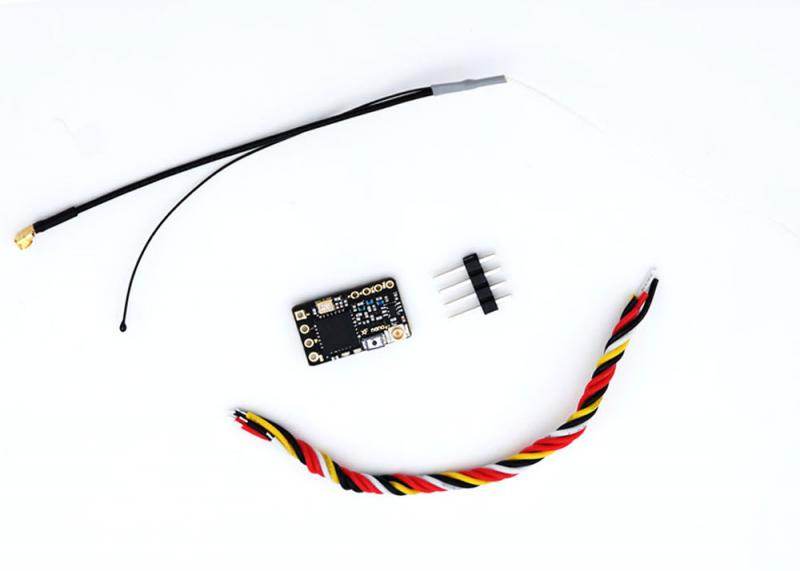
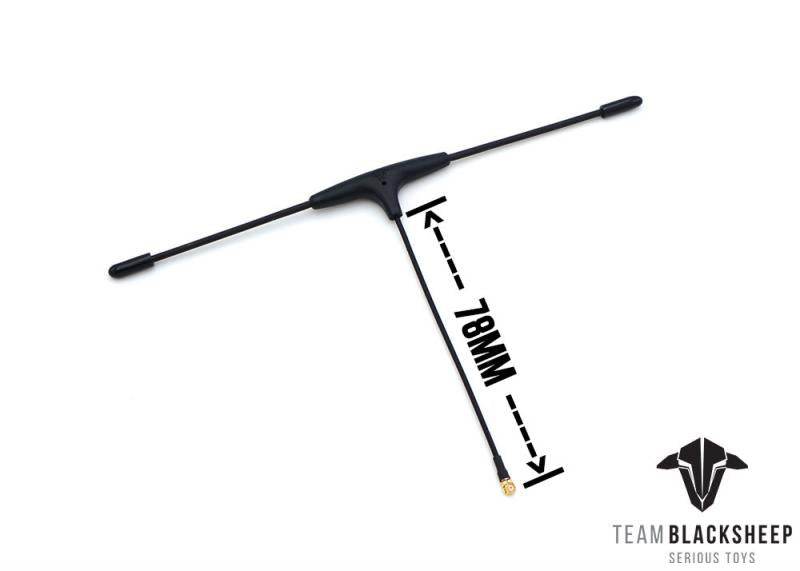
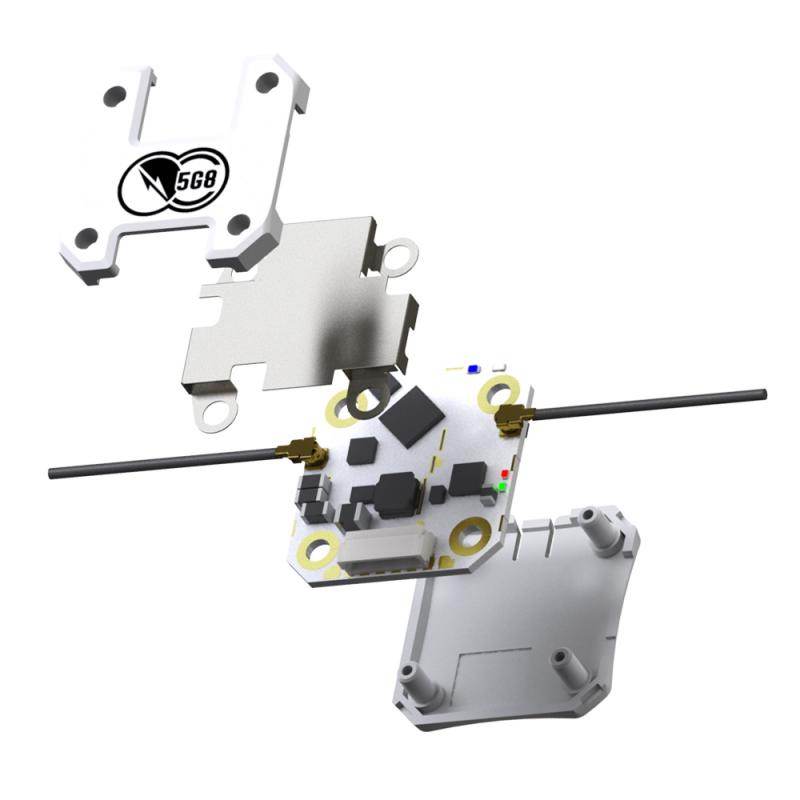
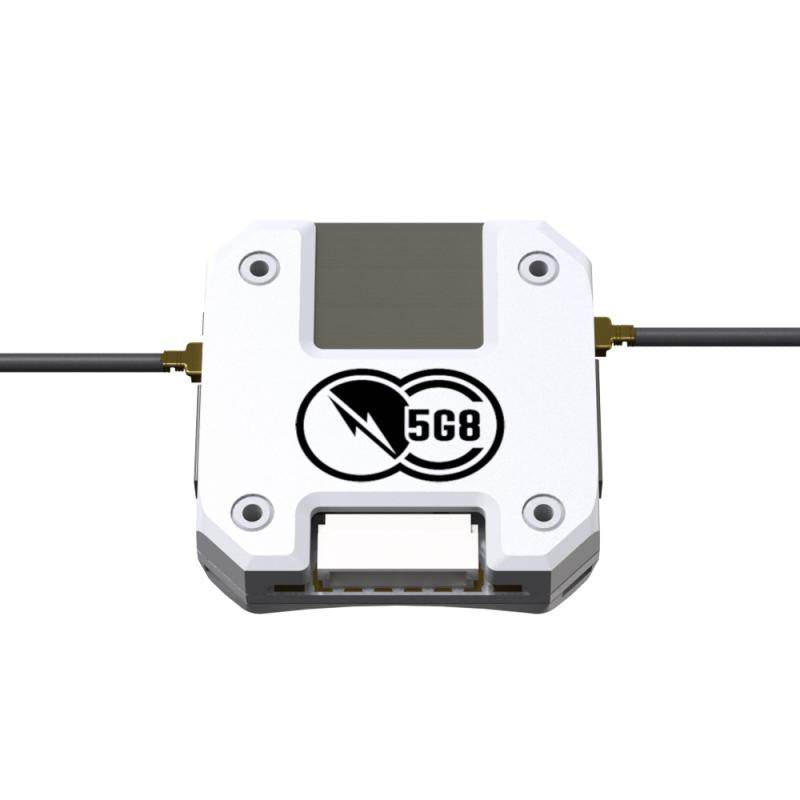
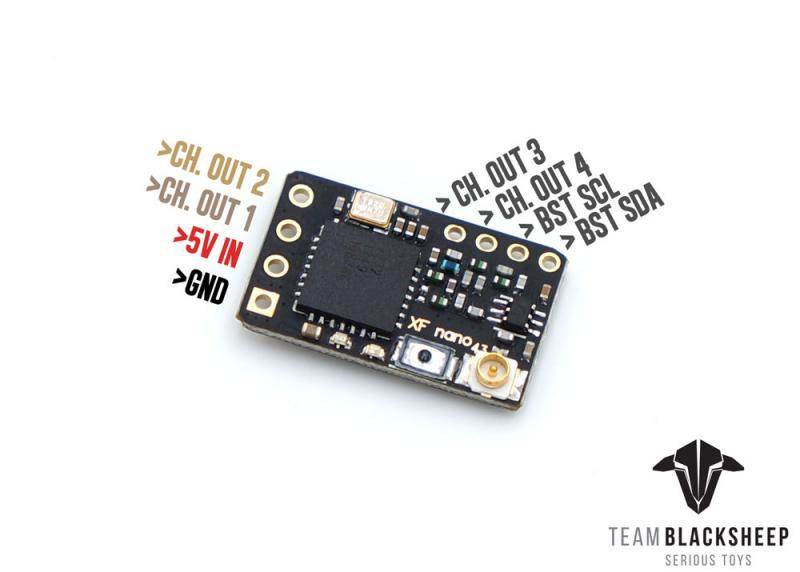
TBS CROSSFIRE DIVERSITY NANO RX - FPV LONG RANGE DRONE RECEIVER
Sale price$89.99 AUD
Regular price$92.99 AUD
Sold out
Save $10.00
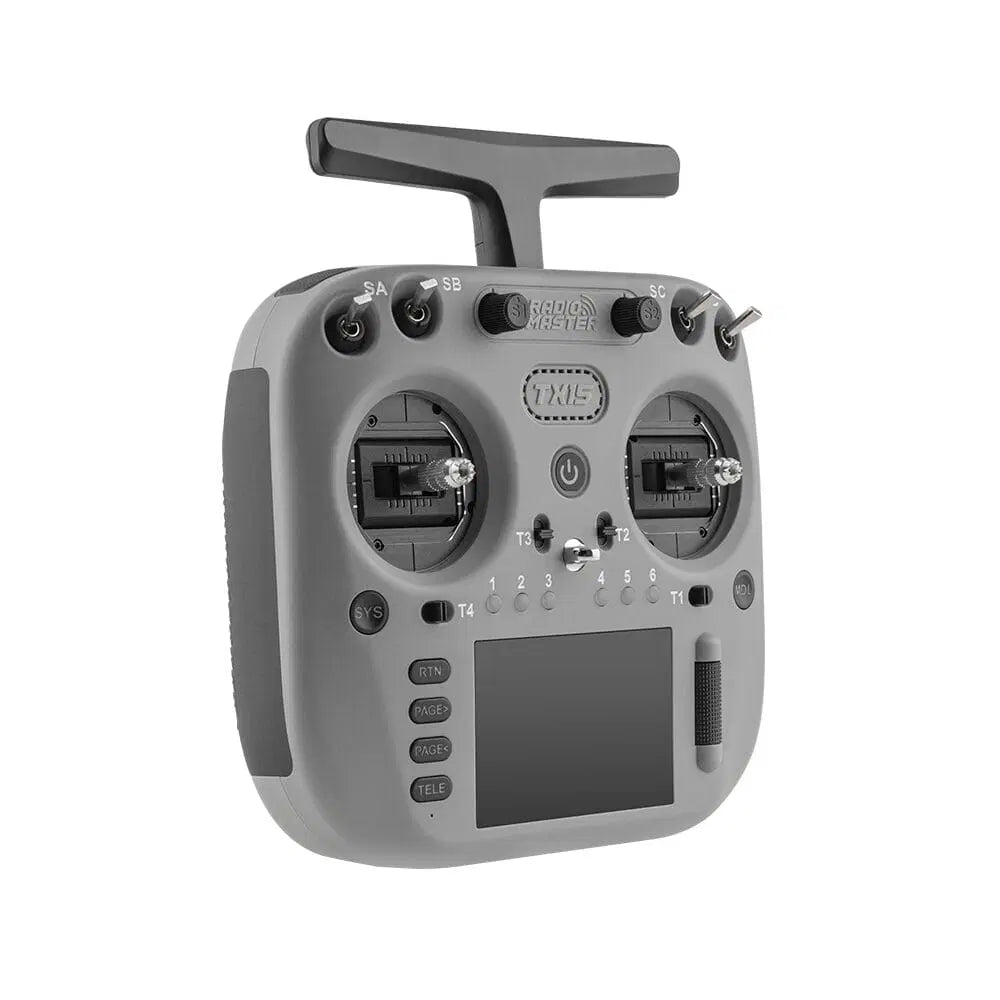
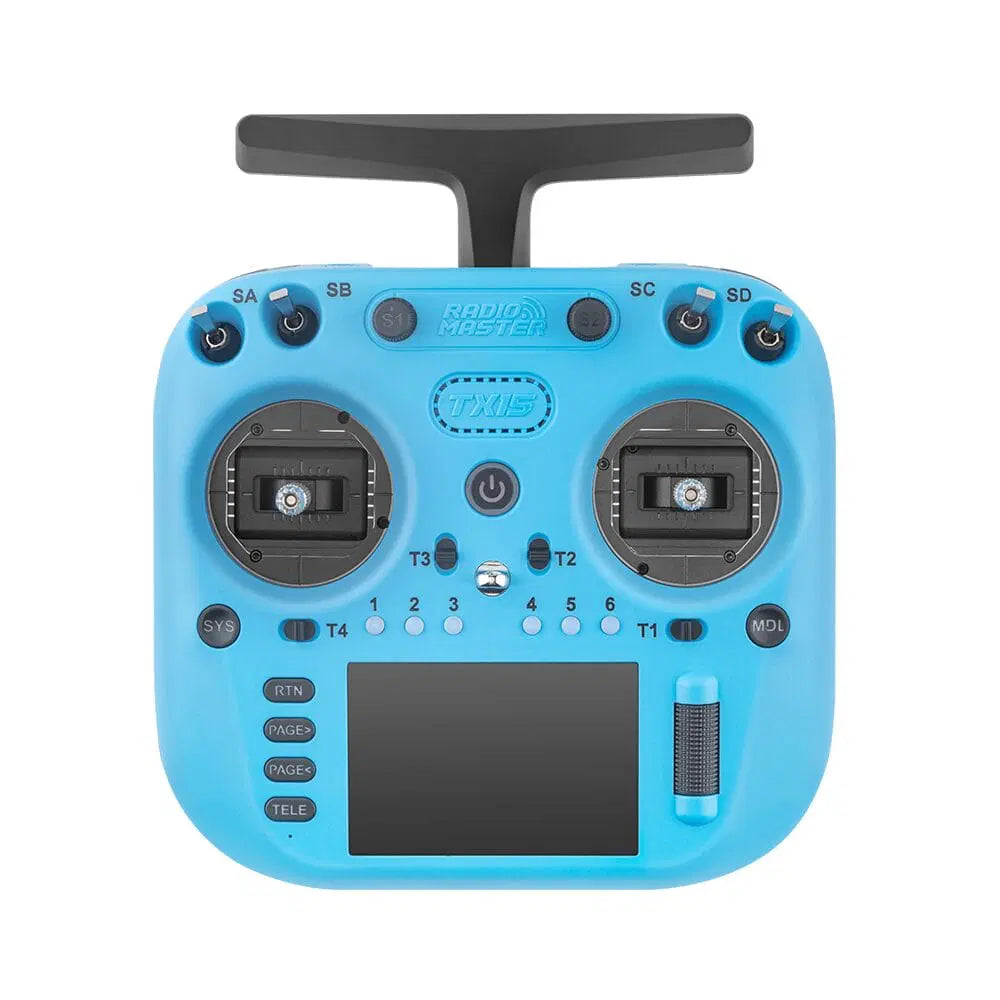


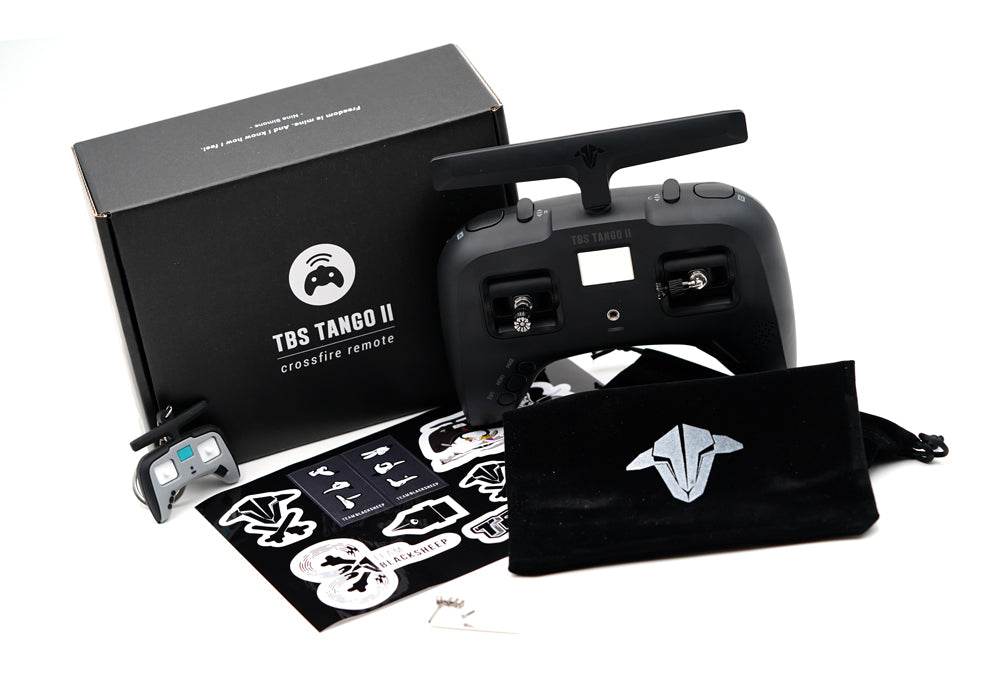
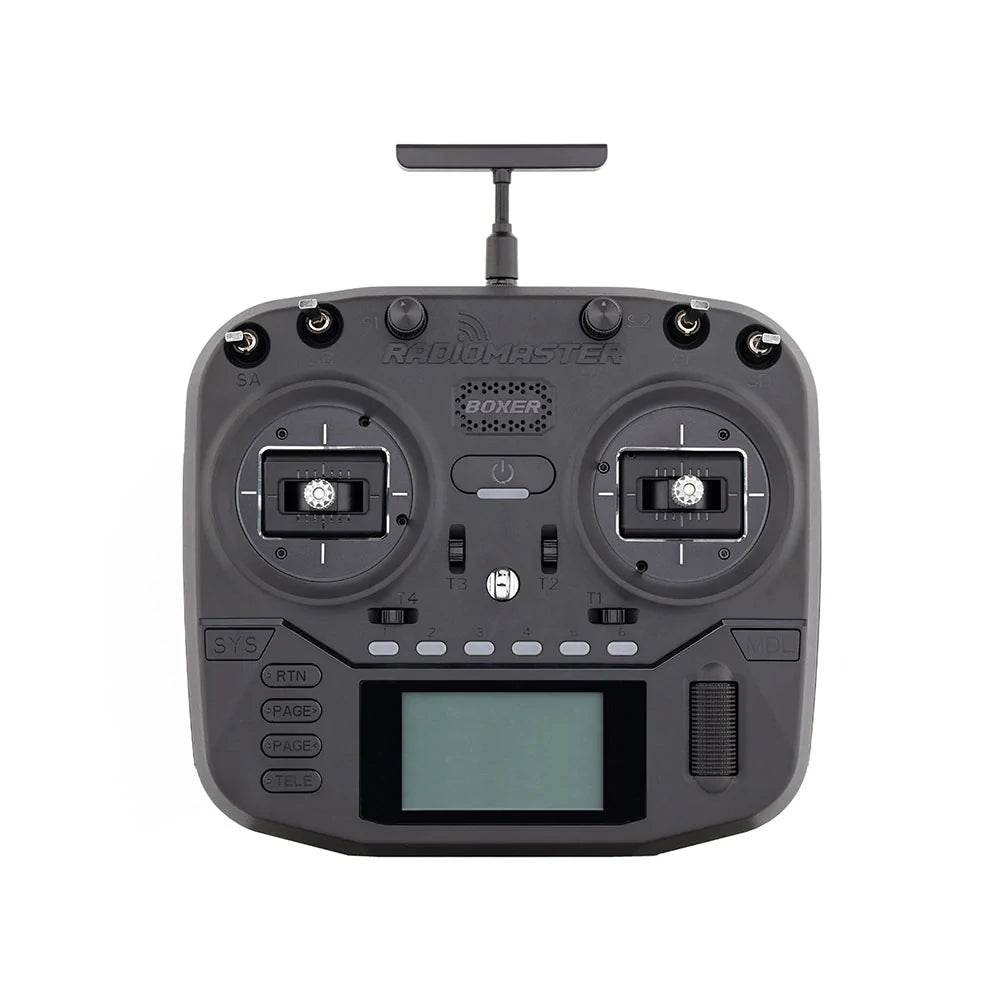
RadioMaster TX15 Radio Controller ELRS Dual-Band
Sale priceFrom $239.99 AUD
Regular price$249.99 AUD
Sold out
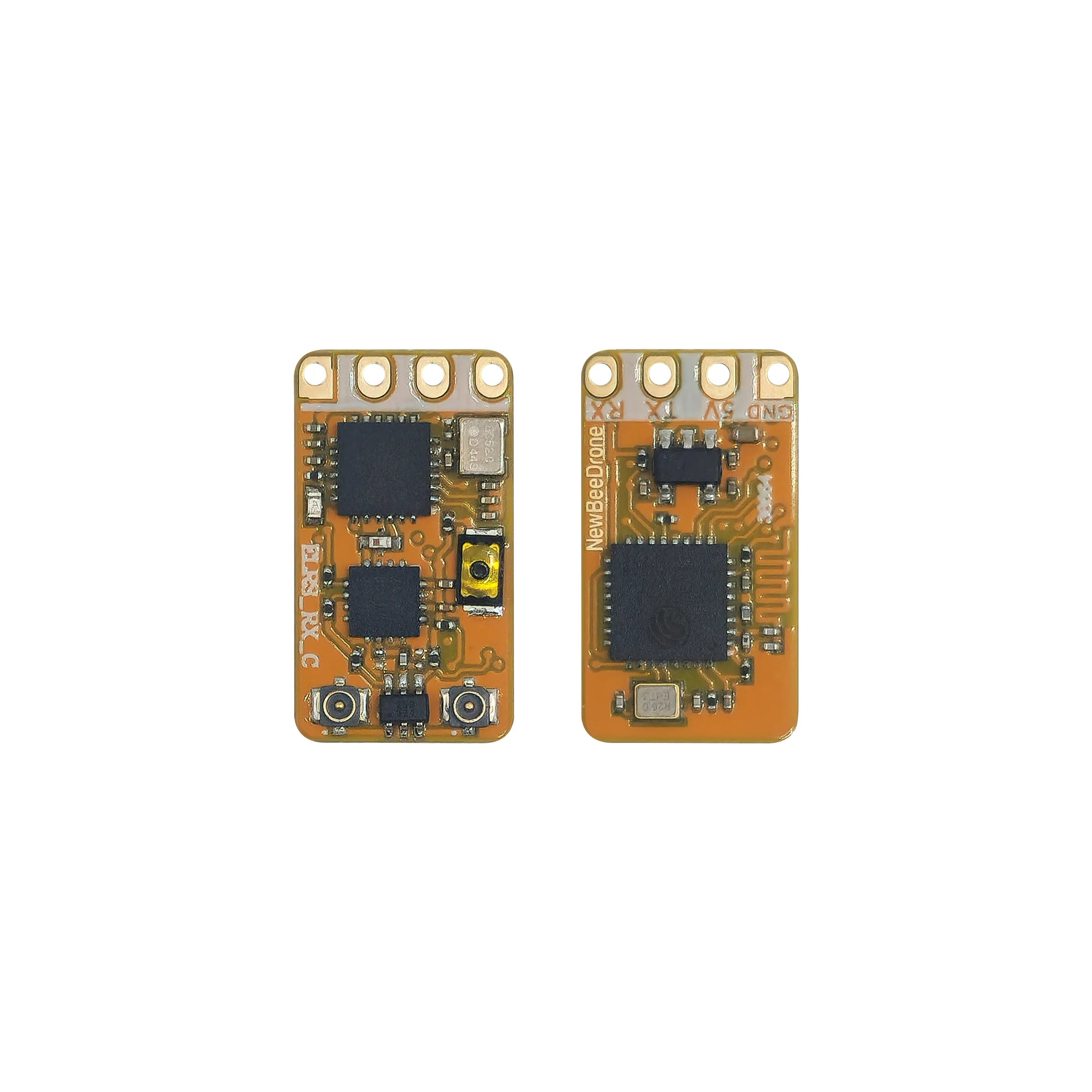
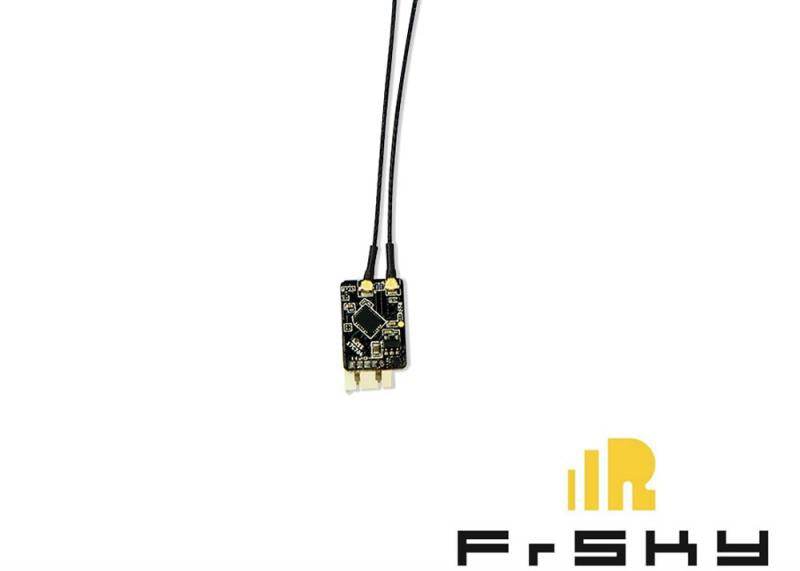
NewBeeDrone BeeCeiver ExpressLRS 2.4Ghz Diversity with TCXO Oscillator Micro Receiver
Sale price$36.99 AUD
Sold out
Filters (0)